Ulf Arnetz, the author of the book Strategy Acceleration, is passionate about trends affecting business strategy execution. In this post, we’ll explore some future-spotting on business agility.
What does the future look like? Which of the trends of today will have taken hold in the companies of tomorrow? We allow ourselves to look into the crystal ball and based on our experiences make some predictions about the future.
This blog series is about strategy acceleration — a new and modern way to execute strategies. It is obvious that we truly believe in strategy acceleration as a method. We believe that focus on better control and measuring will increase. Using tools to measure both outcome and progress will most likely be integrated into every organization. We have just seen the beginning of this.
We predict that Business Agile is a trend that will grow exponentially and many more companies will adopt the Business Agile philosophy and implement it within their organizations. (We have interviewed some people at ICA that you will get to know later in the blog series where they discuss ICA’s way of working with agile methods.)
You have surely heard of or been in contact with agile development. You may have heard the expression Business Agile and is curious about it? Or it might be completely new to you. It is a very interesting growing trend and we will describe it and why it is so interesting to companies.
What is agile development?
To explain what Business agile is we need to start by explaining where the concept agile comes from and what it means. Agile Software Development (or “Agile” for short) is a common approach for a group of agile methods. The basic idea with agile methods is that a modern and fast-moving market demands development methods that can handle change in real-time. Agile philosophy has been an important part of software development for many years.
The agile approach was created in 2001 by a team of programmers who were fed up with all the failed development projects. They reacted to all the failed IT development projects, unrealistic project plans, and the huge focus on documentation. There was overconfidence that the customer knew exactly what they wanted and would therefore be able to create an adequate list of requirements for the whole system even before the project started. Today we know that this is nearly impossible. The lack of communication between customers and contractors also contributed to the desire for a new way of cooperating.
Based on this, the now world-famous “The agile manifesto” was created.
The Agile Manifesto
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Working software over comprehensive documentation
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following a plan
Source: The agile manifesto
During the last few years other functions within companies — areas outside of software development — have looked at the agile way of working and realized that it contains a lot of benefits. There are many articles about new working methods called Agile HR, Agile budgeting, Agile project management, Agile leadership —the list goes on! And now the new trend—Business agile.
What is Business agile?
In short, being Business agile means being able to adjust the organization quickly based on changes in the world and in the market. The need to become more Business agile is urgent, to say the least. More and more industry analysts and institutes argue that companies that are unable to quickly adjust will lose out to the competition faster than what many business leaders think.
Business agile means that the whole organization participates in the agile way of working, not only the IT department, which works with agile development.
The main advice to make the company agile is to transition from long-term plans to focusing on the activities that are most important. To direct the organization towards achieving the two or three strategic initiatives that have the highest priority. A good rule of thumb is to carry these initiatives out in iterations of approximately six months. In order to achieve this the organization needs to know the following:
- Which strategic initiatives are high priority right now and which concrete and measurable goals do they translate into?
- Which weekly, important activities should every employee accomplish in order to drive the change and the execution of the strategic initiatives?
- A tool to follow up on the progress towards the strategic initiatives—for each individual team and for the company as a whole.
In practice, this means two things. Firstly, that the whole organization works towards the execution of the prioritized strategic initiative, or initiatives. Secondly, the CEO or the management can quickly adjust the organization if the priorities need to change. This means that if the most important goal changes for the organization, it is quickly broken down into changed goals and activities. This is so that each employee quickly knows what to do in order to contribute to the execution of the new priority.
Do you recognize this? We hope so, because this is exactly what this blog series is about. To implement strategy acceleration as a working method for strategy execution contributes to your company becoming Business agile.
This image demonstrates four different ways of running a company
In research done by the given sources, only 12% of today’s companies can be called business agile. I.e. they have both the ability to quickly adjust to a changing world (speed index) and at the same time be stable over a long time (stability index).
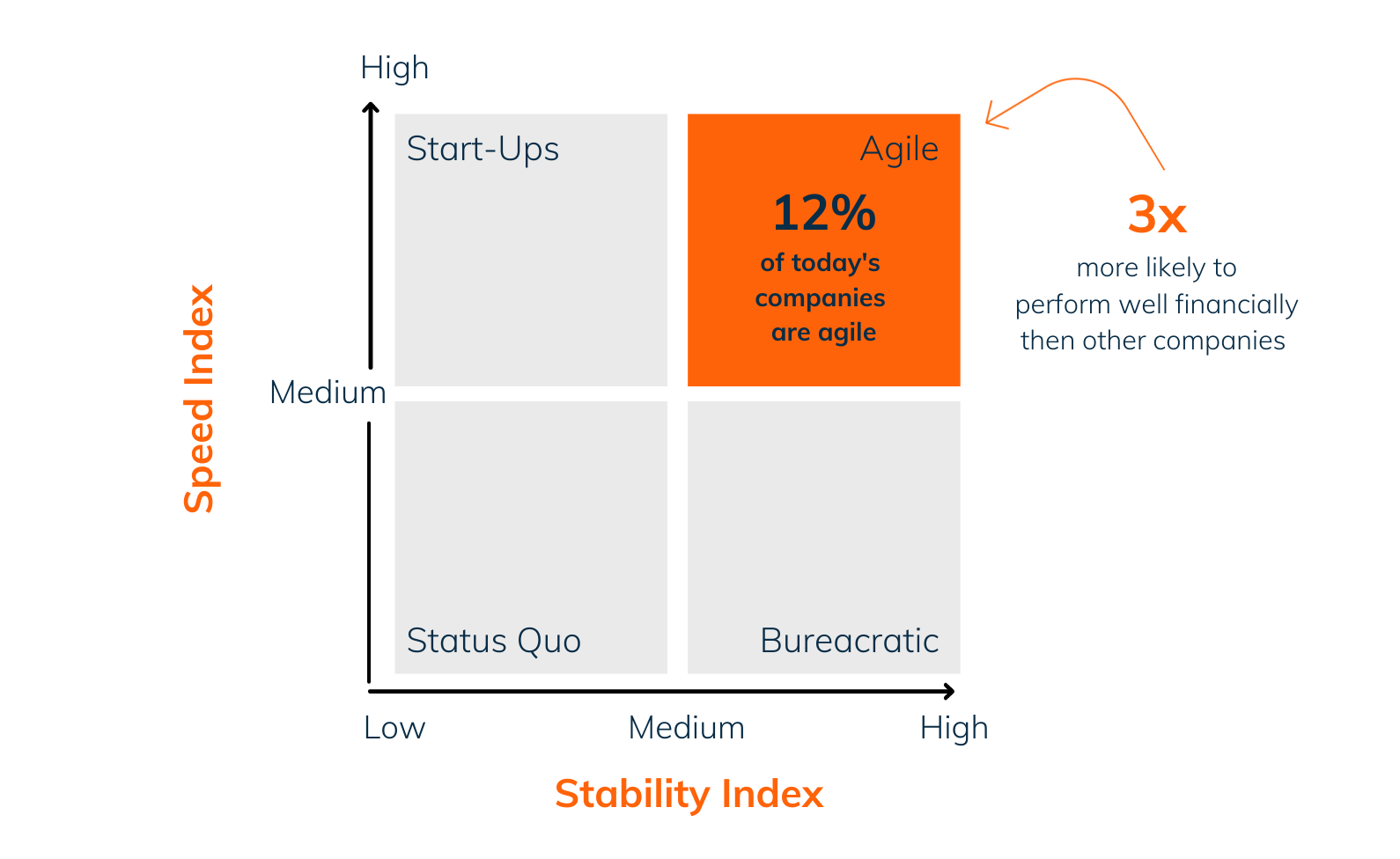
This image demonstrates four different ways of running a company
In research done by the given sources, only 12% of today’s companies can be called business agile. I.e. they have both the ability to quickly adjust to a changing world (speed index) and at the same time be stable over a long time (stability index).
1 | McKinsey & Company – 2018, Reorganizing to capture maximum value
2 | The Economist Intelligence Unit – 2015, Why Good Strategies Fail
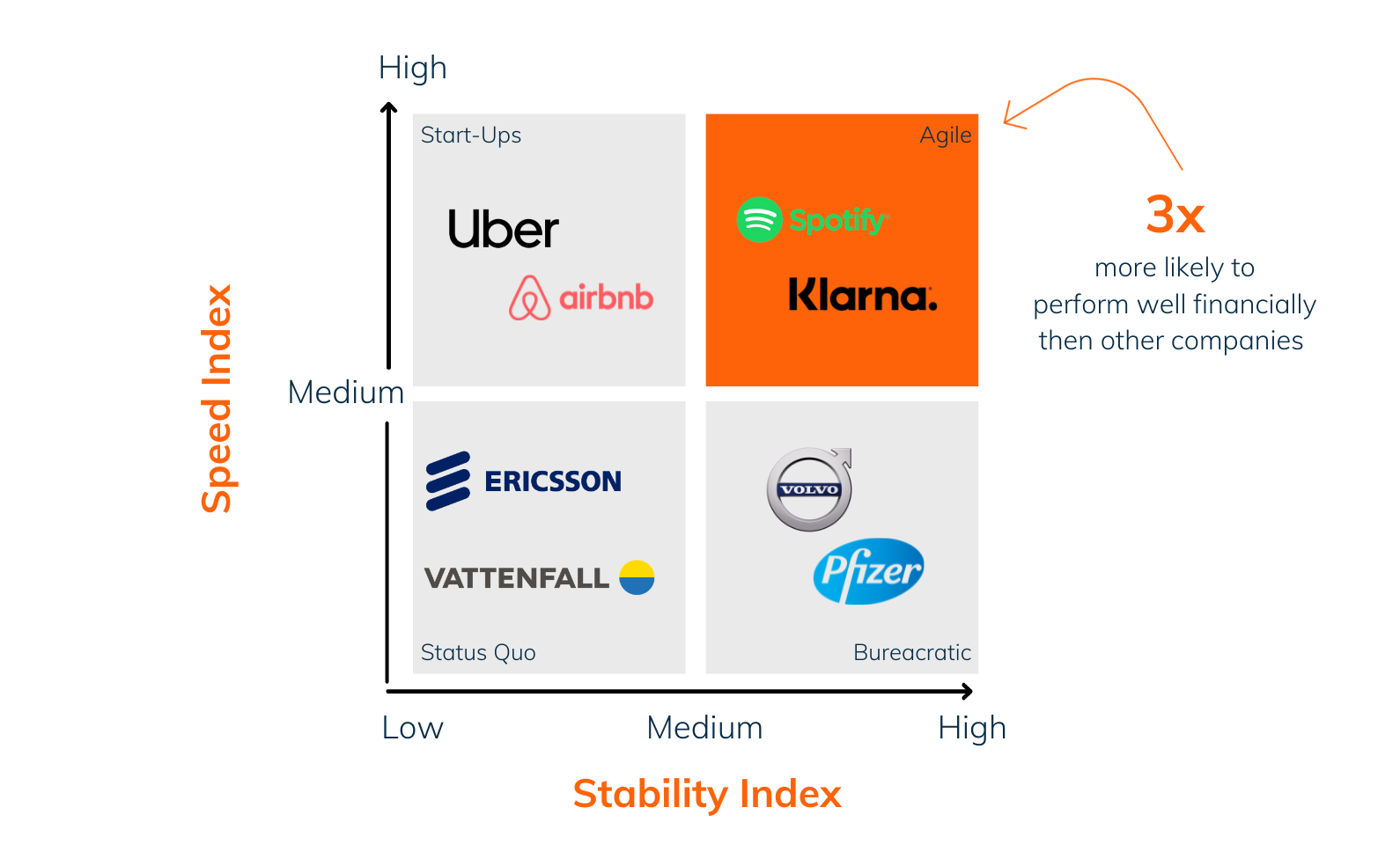
This image shows the model applied to a number of known companies.
Agile companies that execute their strategies faster than their competitors have on average 40% higher revenue growth and 52% higher profit than their industry index.
2 | The Economist Intelligence Unit – 2015, Why Good Strategies Fail
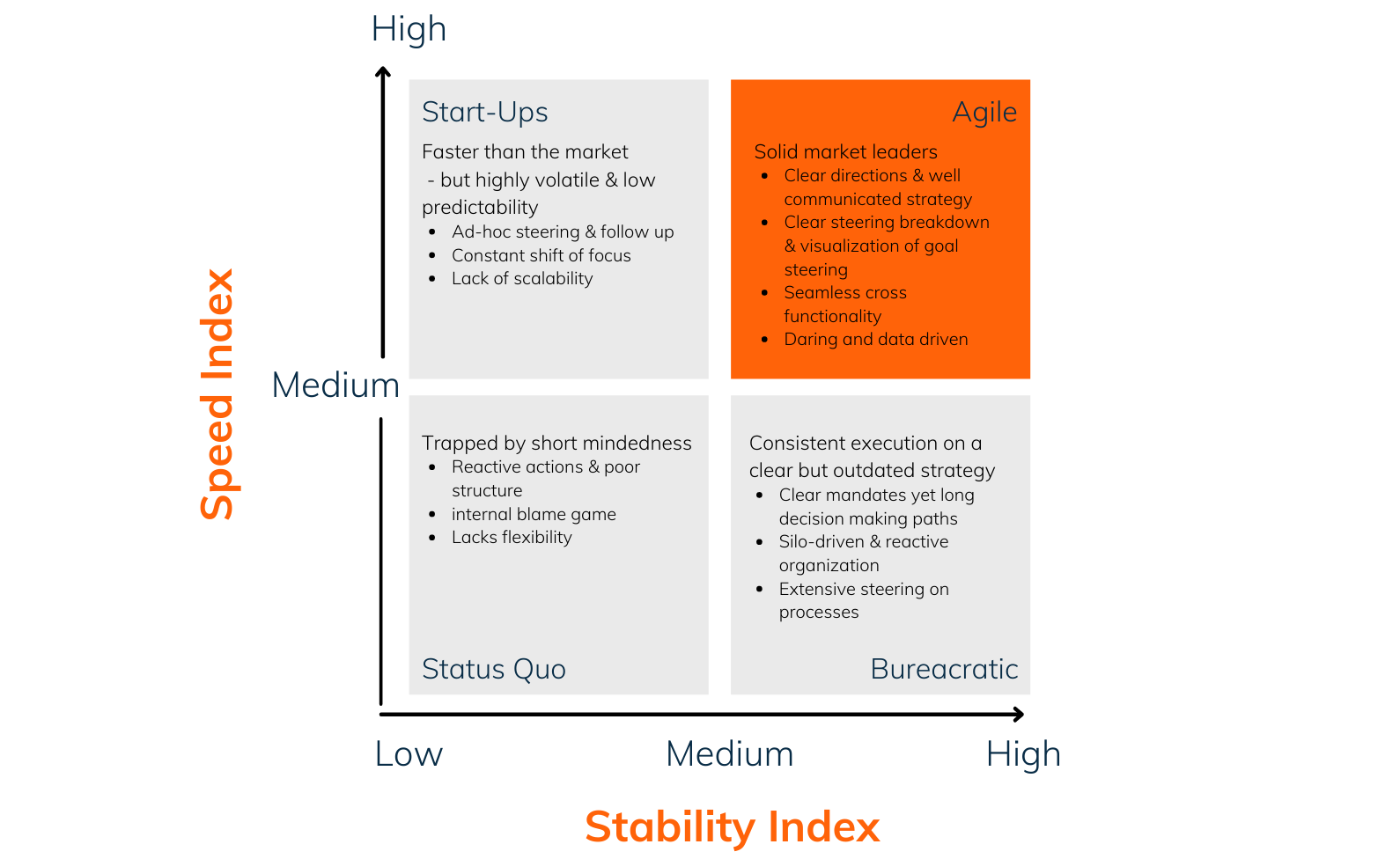
This image shows how the companies in the different boxes work with strategy execution.
Business Agility is about successfully adapting to an ever-changing market by proactively focusing on the most important strategic initiatives.
Why do companies want to be business agile?
In a report from The Economist Intelligence Unit—2015, Why Good Strategies Fail, we can observe that:
”Agile companies that execute their strategies faster than their competitors have in average 40% higher revenue growth and 52% higher profit than their industry index”
For large companies, this is the only way to create a company culture that somewhat minimizes the risk of disruption. It is no guarantee, but currently, it is the best-known model that can truly be implemented and has positive and reasonably predictable financial results.
Future-spotting: Comparison between traditional agile development and business agile?
What are the similarities and differences between traditional agile development and to be business agile?
Similarities:
- Work is structured with priorities and is always asking the question: WHAT IS MOST IMPORTANT?
- Breaking down activities into smaller parts, so that everybody within the company/organization can work towards the same goals in their own way.
- Ownership and commitment. By giving responsibility for HOW things should be done, a high level of involvement is created among those who will execute.
- System support throughout the whole process. Both in IT agile and Business agile the focus is on measuring progress and getting continuous feedback.
Differences:
- In Business agile, the end date is never changed. If you are lagging behind, you immediately add more focus/time. A plan or deadline is never postponed.
- In Business agile, you always set a financial goal and a date for when it will be achieved. In IT agile there are agile iterations, but the overall goal and the deadline for the overall goal are often not decided and can be difficult to determine.
- Starts from a pre-set financial goal at a pre-set date. From there you work backward to “today/this week” and create a plan.
- Often engages the whole company and is often cross-functional—to be compared with IT agile which foremost concerns the customer and those involved in the development.
Strategy acceleration and business agile – how do they fit together?
Strategy acceleration can be described as a skill. To develop the skill to quickly readjust, to change course when the market, customers, and competitors demand it. That is what Business agile is all about. If strategy acceleration is used as a working method and it has been established within the company, a big step has been taken towards becoming Business agile.
Learn more about Business Agility and watch our introduction videos here.
Behind this future-spotting is Howwe. But who is Howwe for?
Do you have several teams, departments, and leaders? And you want to accelerate your growth? Then you will most certainly benefit from Howwe. We’ve seen success across all sectors and industries. Do you want to see some examples? Check out some of our customers or explore some of the other sectors we support below.
We have a proven track record of supporting real estate companies in connecting their business plans to everyday operations. A proactive way of working supported by our SaaS application Howwe enables the full potential of your organization.
Many of the companies we support within the manufacturing and industrial sector struggle with implementation of their interdivisional and global transformation projects. With massive organizations, aligning the whole organization and making the business plan actionable on all levels is challenging.
Howwe supports many of the world’s largest healthcare companies, such as MSD, Amgen and GE Healthcare. Using Howwe, our customers achieve both organization-wide transformation and acceleration of financial results.





